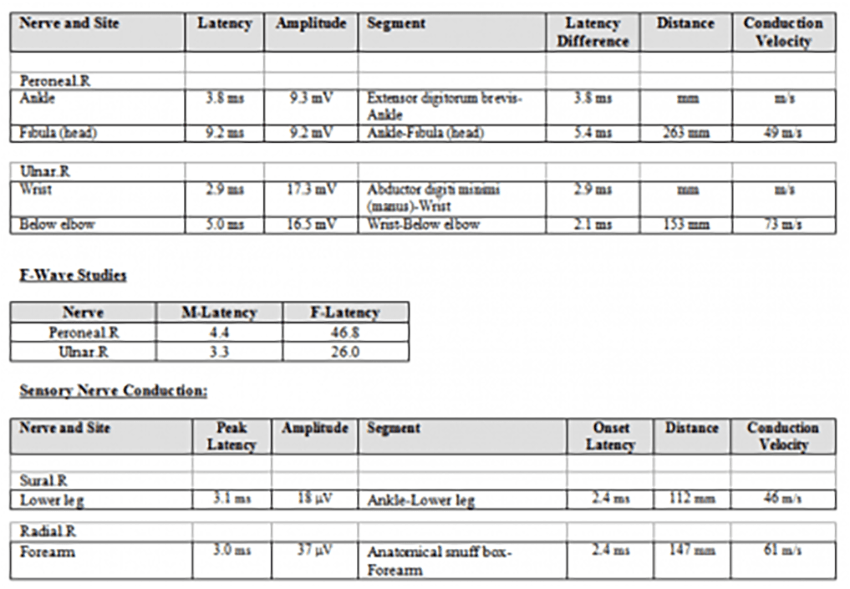
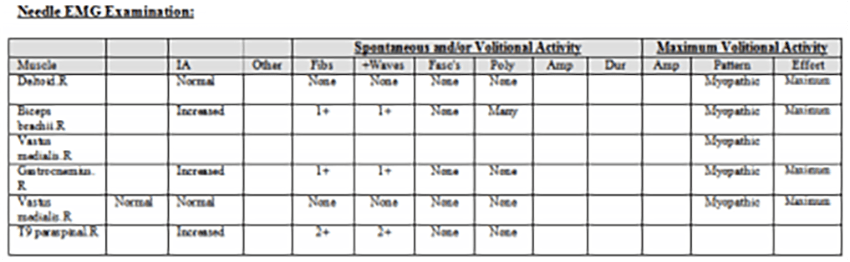
The nerve conduction study was normal. EMG showed diffuse myopathic changes and spontaneous activity (more prominent in the thoracic paraspinal muscles).
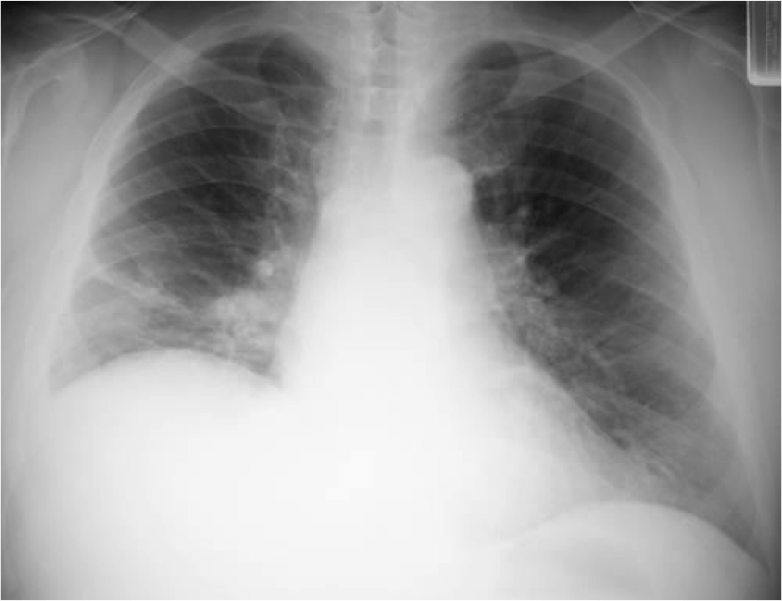
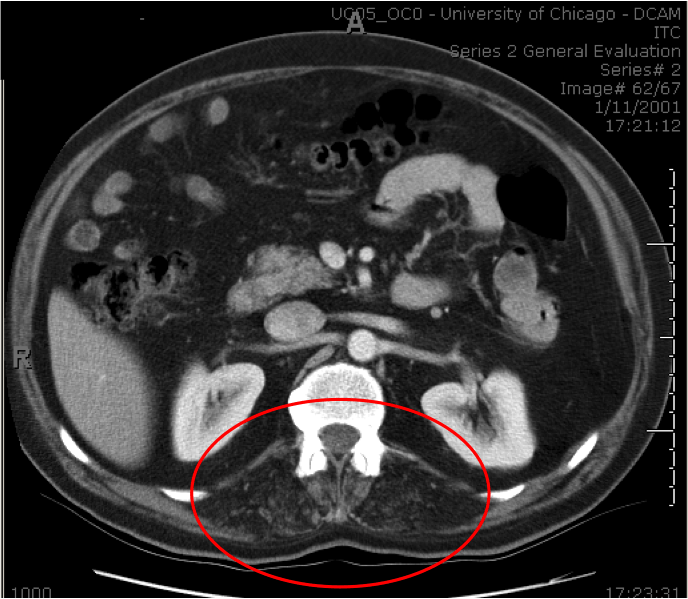
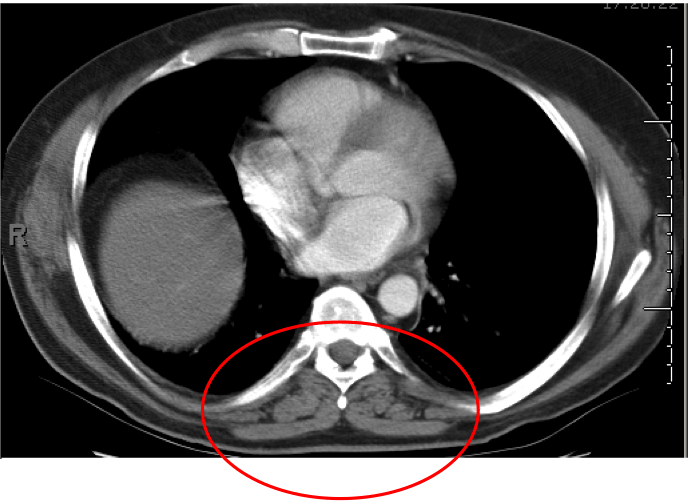
Chest X ray showed elevation of R. hemidiaphragm and passive atelectasis of the R. lower lobe (see A, right column). Seated spirometry showed forced vital capacity (FVC) of 61% predicted, which dropped to 26% predicted when he assumed supine position. Positive expiratory force and negative inspiratory force were 48 cmH2O and -25 cmH20 respectively. The findings of the spirometry indicate significant respiratory muscle weakness, the dramatic drop in supine FVC (compared to seated) indicates severe diaphragm weakness. The latter correlates with the findings on the chest X ray. MRI of the lumbar spine showed severe atrophy of the posterior lumbar paraspinal muscles (see circles area in B, right column, compare with C: normal lumbar paraspinal muscles in another patient’s study).
What is the next step? the diagnosis? (click here).
